
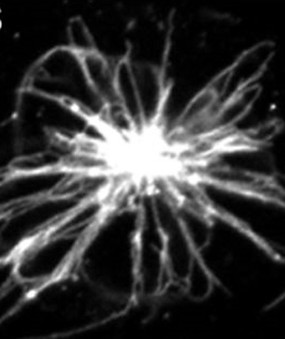
Endocytic network of human dendritic cell upon T cell recognition.
live cell confocal lsm
Lipids, T cells &
Tissue Homeostasis
metabolic distortion with age
In cancer and ageing, tissues become metabolically distorted and enriched in stressed (senescent) cells that release bioactive lipids and inflammatory signals into their environment. These lipids accumulate in age-related pathologies and genetic disorders (e.g. X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, Zellweger syndrome) that are characterised by premature tissue degeneration, chronic inflammation, fibrosis, and stem cell dysfunction—indicating that these lipids act as causal metabolic stressors.
Our research focuses on how lipid metabolic perturbations reprogram T cells, particularly regulatory T cells, and reshape their function with profound consequences for immune surveillance in ageing and cancer. We use advanced microscopy to dissect how lipid-rich, senescent tissues instruct immune cell behaviour at the molecular and cellular level.
Our imaging reveals that lipid-driven immune reprogramming is accompanied by striking structural remodelling and reorganisation of:
• The 3D endocytic network (the intracellular transport system) – Fig. 1
• Mitochondria (the cellular energy factories) – Fig. 2
• The nanoscale organisation of T cell receptors (the “on-button” of T cells) – Fig. 3
• Plasma membrane lipid and protein composition and 3D architecture at the immune synapse – Fig. 4
By integrating immunometabolism, lipidomics, and immune cell engineering with high-resolution imaging and tissue-mimetic platforms, we aim to define how metabolic signals from senescent tissues drive immune plasticity. Our long-term goal is to uncover general principles of immune–tissue communication and exploit them to restore immune surveillance and tissue homeostasis in cancer and age-associated disease.
T cell mitochondria (orange) shaped by cytoskeleton (green) next to nucleus (blue).
3D SIM

Clusters of T cell receptor molecules
at the site of cell-cell communication. PALM

T cell actin (green) and microtubule (magenta) remodelling during cell-cell contact.
LLSM

T cell mitochondria.
Expansion microscopy
RECENT ARTICLES
Autophagy-regulated mitochondrial inheritance controls early CD8+ T cell fate commitment.
Borsa, M., Lechuga-Vieco, A.V., Kayvanjoo, A.H. Jenkins E, Yazicioglu Y, Compeer EB, Richter FC, Rapp S, Mitchell R, Youdale T, Bui H, Kuuluvainen E, Dustin ML, Sinclair LV, Katajisto P, Simon AK.
Nat. Cell. Biol. 2026 link to open access article
